XLPE Insulated LV Power Cable is a kind of XLPE cable, which plays an important role in power supply network. Enough attention should be paid to the operation of XLPE power cable lines, especially to the safety and reliability of cable accessories. Necessary and appropriate measures must be taken to prevent accidents and monitor the operation of power cable lines. The test scheme of XLPE cable mainly includes withstand voltage test, conventional condition assessment and partial discharge detection, and the partial discharge detection is the main one that can be used for cable test in field operation.
The cable is composed of multiple parts and multiple materials.
1. Conductor core wire
The role of the conductor core wire is to act as a conductor and transmit electrical energy. There are two kinds of materials for the conductor core wire in the cable:
- Copper, as a commonly used excellent conductor, has the advantages of large conductivity, high mechanical strength, easy processing, corrosion resistance, etc., and is widely used as cable core;
- Aluminum is also one of the commonly used metal materials for power cable conductors. It is rich in resources and has a lower price than copper, but its resistivity is higher than copper, and the line loss is larger. It is mostly used for low-voltage cables.
The core conductor structure generally adopts multi-core round stranded wire. The round wire makes the conductor electric field uniform, which is beneficial to improve the voltage level. The twisting of multiple wires increases the flexibility and bending of the conductor.
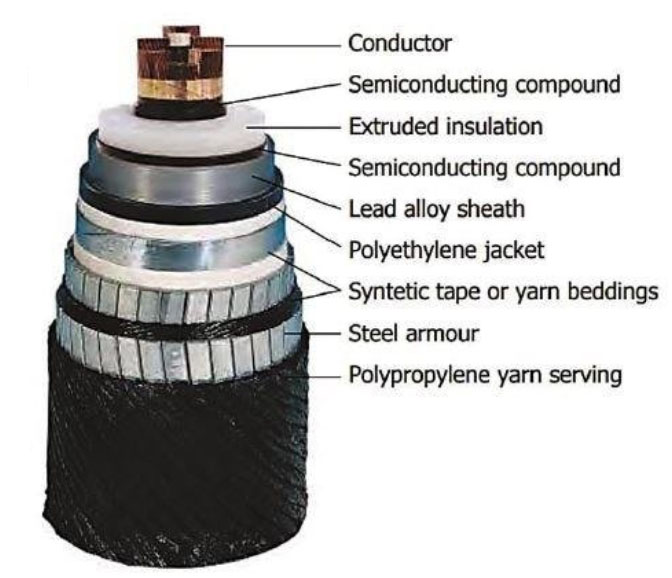
The cable runs under the condition of high voltage and high field strength. In order to avoid the electric field concentration and prevent the wire effect, the compressed core should be used. In addition, the compressed core can prevent the semiconductor from entering the core when the semiconductor shielding layer is extruded. It can also effectively prevent moisture from entering along the core.
2. Semiconductor shielding layer inside and outside insulation
At present, cross-linked polyethylene with carbon black is used for semiconductor shielding layer wires inside and outside the insulation. In the early stage, the outer semiconductor shielding layer of cross-linked cable was also formed by wrapping with graphite cloth, but this structure has poor performance. With the development of extrusion technology of inner and outer semiconductor shielding layer and insulating layer at the same time, the wrapped shielding structure has been eliminated. When selecting cables, the wrapped shielding structure should not be used as far as possible. The volume resistivity of semiconductor shielding layer is generally below 10000 Ω· cm, and its thickness is generally 1-2mm. The semiconductor layer contains colloidal carbon, which can play the role of uniform electric field. At the same time, carbon can absorb the spoilage produced by air ionization in the small gap of the cable body, uniform electric field, and protect the cable insulation.

3. Cable metal shielding layer (metal sheath)
The cable metal shielding layer, also known as copper strip shielding, is used to provide a circuit for the cable fault current and a stable ground potential, so that the electric field direction is the same as the insulation radius direction. When the cable fails, the copper strip acts as a short-circuit fault current circuit to bear the unbalanced current and prevent the axial surface discharge. The cross section of copper strip (wire) can be selected according to the size of fault current, duration and whether the grounding is one end or two ends. Single core and three core XLPE cables with voltage grade of 35kV and below are provided with steel strip as armor layer for mechanical protection. Corrugated aluminum (copper, lead, stainless steel) sheaths are used as armor and inner waterproof sheaths for 110 kV and above XLPE cables. Because the water absorption of PE or PVC sheaths is 0.01% and 0.15% – 1% respectively, and the metal is almost impermeable, the impermeable metal inner sheaths are used for ultra-high voltage cables. In addition, in the inner sheath of the ultra-high voltage cable, there are waterproof tape and other waterproof technology, which makes the water that has entered difficult to diffuse.
4. Sheath
XLPE cable sheath is usually made of PVC or PE material, and the thickness is generally 3-4mm. But PVC material is generally used, because the fire retardant performance of PVC material is better than that of PE. But the water absorption of PE is less than that of PVC. In order to reduce water seepage, some manufacturers use PE material to make outer sheath. For the outer sheath of 110 kV XLPE insulated cable with ultra-high voltage, due to the requirement of withstand voltage, it is necessary to check whether the conductive layer is complete during the cable acceptance, otherwise the test of sheath will be meaningless.

